Mexico's manufacturing sector has established itself as a cornerstone of the country's economic growth and its positioning in international trade, despite the tariff frictions that began in 2025. Indeed, manufacturing exports have been the driving force behind the Mexican economy for decades, transforming the country from a raw materials-based economy to an emerging industrial power.
The history of manufacturing in Mexico is a narrative of transformation and adaptation. Since the mid-20th century, the country has undergone significant evolution in its approach to industrial production and exports.
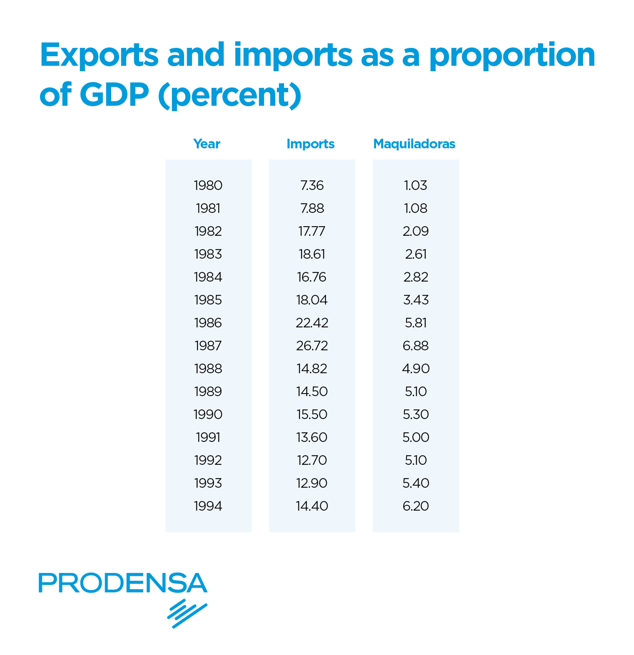
From the 1940s to the 1970s, Mexico adopted the import substitution model, an economic strategy designed to reduce dependency on foreign products and promote domestic industrialization. While this protectionist approach initially stimulated domestic industrial growth, it eventually revealed limitations in global competitiveness and productive efficiency.
Impact of NAFTA/USMCA on the Manufacturing Sector
The signing of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) in 1994 marked a turning point for Mexico's manufacturing sector. This agreement opened new market opportunities, primarily with the United States and Canada, driving a wave of foreign direct investment into Mexican manufacturing.
NAFTA, now renewed as the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), has been crucial for Mexico's integration into global value chains, facilitating the creation of highly specialized industrial clusters, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and more recently, semiconductors.
Recent data from the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) confirms the narrative. The Mexican manufacturing sector is characterized by its diversity and increasing sophistication. Key sectors contributing to manufacturing exports include:
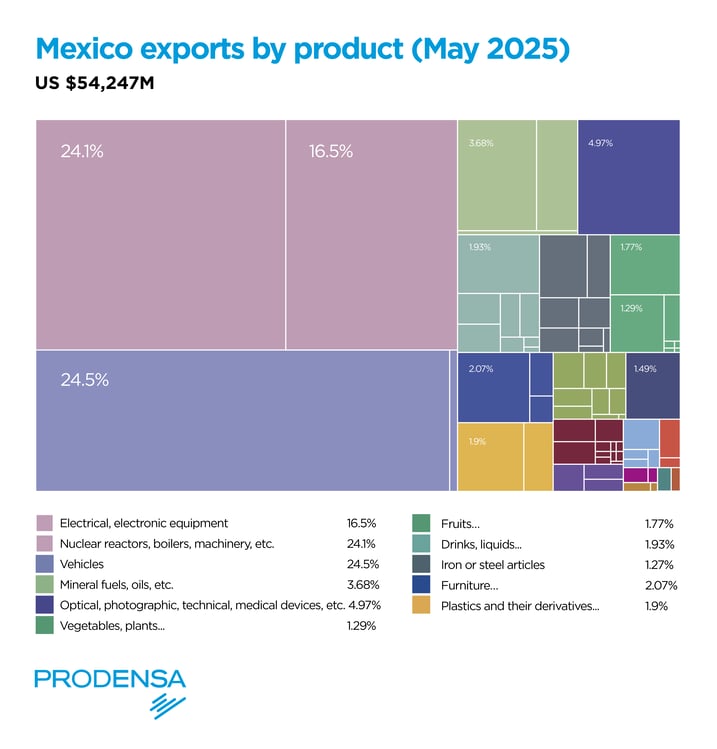
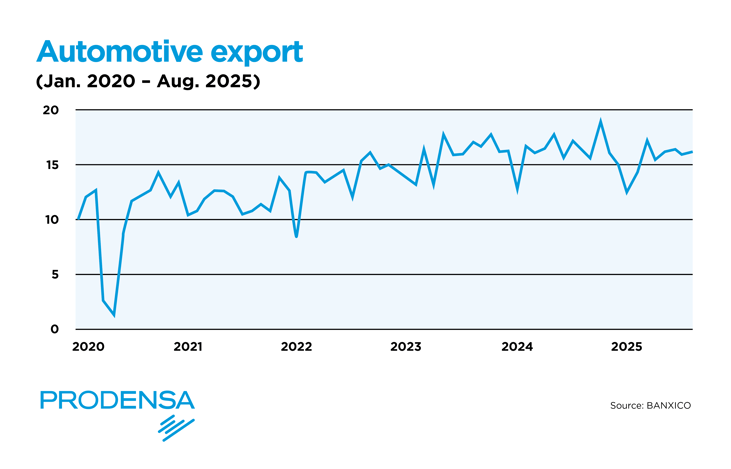
- Automotive: This sector represents approximately 24% of the country's total exports and almost 4.5% of the national GDP. It has shown robust growth despite the sectoral tariffs imposed by the US administration.
- Electronics: Including the production of electronic components, computers, and communication equipment.
- Aerospace: A rapidly growing sector, with Mexico emerging as a significant hub for aerospace component manufacturing.
- Machinery and Equipment: Encompassing a wide range of industrial and consumer products.
- Chemical and Plastic Products: A diversified sector including pharmaceuticals and construction materials.
The geographic distribution of manufacturing production in Mexico is strategically spread across the country, with significant concentrations in:
- North: States like Nuevo León, Coahuila, and Chihuahua benefit from their proximity to the United States.
- Center: The Bajío region, including Guanajuato and Querétaro, has become an important automotive and aerospace cluster.
- Central-West: Jalisco, known for its electronics and information technology industry.
These important states are included in our report about industrial corridors in Mexico made by Alejandro Mendoza, Prodensa’s President of Real Estate Solutions.
Upward Trend in Manufacturing Exports
Mexico's manufacturing sector has shown sustained growth over the last decade, with some fluctuations due to global economic factors. However, INEGI data reveals that manufacturing exports have maintained an upward trend, with particularly notable growth in recent years.
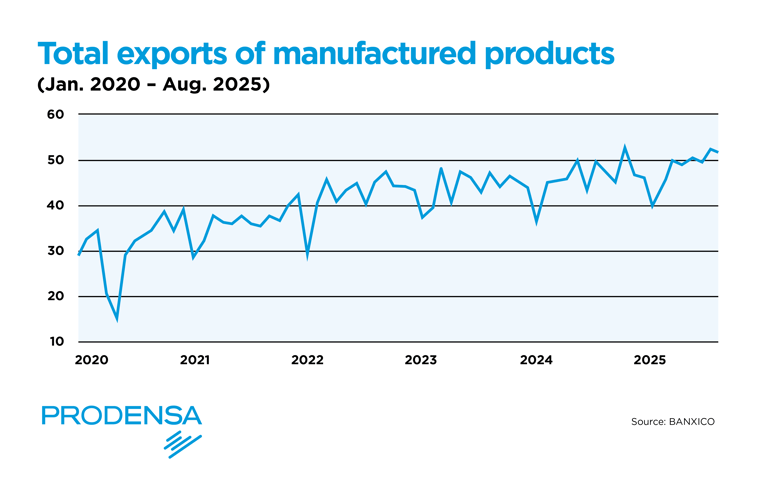
In August 2025, year-over-year growth in non-oil exports was driven exclusively by manufacturing, which grew at an annual rate of 8.85%. Overall growth in non-oil exports was explained by the manufacturing component, which posted annual growth of 9.01%, largely driven by non-automotive manufacturing exports, which increased 14.39% year over year. This increase is particularly significant given the challenging global economic environment.
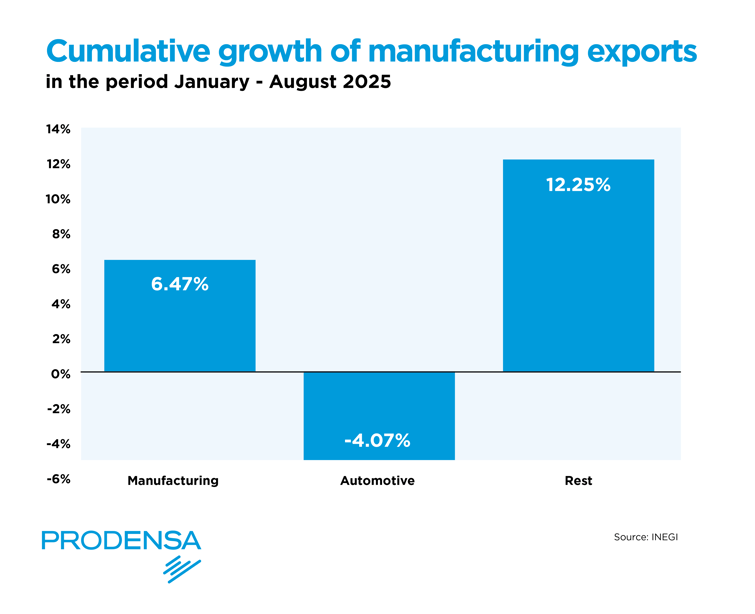
While other export sectors, such as oil, have experienced volatility, manufacturing exports have proven to be more resilient and consistent in their growth. In fact, the cumulative growth of total exports in 2025 is largely explained by manufacturing exports, with the manufacturing sector posting cumulative growth of 6.47%.
Contribution to GDP and Total Exports
Manufacturing exports play a critical role in Mexico’s economy, representing a significant share of national GDP and accounting for the majority of the country’s total exports. As of August 2025, manufacturing exports excluding the automotive sector accounted for 62% of Mexico’s total exports—their highest share for a comparable period since 2009—and 68.11% of total manufacturing exports.
“This dynamic is largely explained by the fact that tariffs imposed by the United States on Mexico under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA) are not being applied strictly, while sector-specific tariffs affecting the automotive industry are being enforced,” according to Banco Base. “As a result, automotive exports have accumulated a contraction in 2025, while non-automotive manufacturing exports are posting growth of 12.25%.
Main Destinations for Mexican Manufacturing Exports
The United States remains the primary destination for Mexican manufacturing exports, benefiting from geographical proximity and trade agreements. Canada, as part of the USMCA, is also a significant trade partner.
83.99% of Mexico’s non-oil exports between January and August 2025 were destined for the United States, accumulating growth of 6.1%. This growth was largely driven by non-automotive exports, which posted cumulative growth of 11.6%.
Non-oil exports to the rest of the world recorded cumulative growth of 6.5% compared to the same period in 2024, with non-automotive exports increasing by 9.7%.
Additionally, Mexico has diversified its export markets, including:
- European Union: Especially in sectors such as automotive and aerospace.
- Asia: With growing interest in countries like China and Japan.
- Latin America: Leveraging regional trade agreements.
Future Outlook: Navigating Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
While the 2025 landscape highlights the resilience and momentum of Mexico’s manufacturing sector, medium- and long-term performance will depend on the country’s ability to capitalize on global trends while navigating key strategic challenges.
The following factors will shape the next phase of growth for Mexico’s manufacturing exports.
1 Nearshoring Consolidation and the Investment Opportunity
The trend toward supply chain relocation, or nearshoring, is far from reaching its peak. Mexico is well positioned to continue attracting investment driven by the need for resilience, proximity to the North American market, and logistical certainty. According to analysis by the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), nearshoring could generate up to $35 billion USD in additional annual goods exports for Mexico.
To fully capture this opportunity, continued investment in infrastructure—industrial parks, energy, and logistics—is essential, along with regulatory simplification to facilitate new business entry, particularly in high-technology sectors such as semiconductors, medical devices, and electric vehicle components.
2 The 2026 USMCA Review
A key milestone on the horizon is the scheduled review of the United States–Mexico–Canada Agreement (USMCA) in 2026. This process will assess the agreement’s performance and represents both an opportunity to strengthen regional integration and a potential risk if significant disputes arise.
Mexico must be prepared to demonstrate full compliance with its commitments, particularly in labor standards, environmental provisions, and automotive rules of origin.
3 The Transition to Electromobility and Sustainable Manufacturing
The automotive sector—one of Mexico’s export pillars—is undergoing a global transformation toward electromobility. Mexico’s future success will depend on its ability to attract investment not only in electric vehicle assembly, but across the entire value chain, including batteries, software, and electronic components.
At the same time, growing global demand for sustainability and ESG compliance will require Mexican manufacturers to adopt cleaner production processes, increase the use of renewable energy, and improve product circularity—turning sustainability into a critical competitive advantage rather than a compliance obligation.
4 Technological Sophistication and the Talent Challenge (Industry 4.0)
To avoid competing solely on cost, Mexico’s manufacturing industry must accelerate its transition toward Industry 4.0. Automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), data analytics, and artificial intelligence are tools that will increase efficiency and enable the production of goods with higher added value.
This technological leap, however, brings with it the challenge of developing the necessary talent. It will be essential to strengthen collaboration between the private sector, universities, and government in order to train the engineers, technicians, and specialists required by this new industrial era—ensuring that Mexico not only assembles, but also designs and innovates.
We can conclude that manufacturing exports continue to be Mexico’s economic engine, demonstrating adaptability and resilience in the face of global challenges. However, sustained investment in innovation, infrastructure improvements, and the deepening of trade relationships will be critical to maintaining and expanding Mexico’s position as a global manufacturing leader in the years ahead.

 Manufacturing Exports:
Manufacturing Exports:
Goods produced through industrial processes—such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, machinery, and chemicals—that are sold abroad. In Mexico, manufacturing exports represent the backbone of international trade and a key driver of GDP growth.
Nearshoring:
The relocation of manufacturing closer to end markets—especially within North America—to reduce risk, improve resilience, and meet USMCA requirements.
Industry 4.0:
The integration of automation, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and connected systems into manufacturing. Industry 4.0 enables higher productivity, greater value-added production, and long-term competitiveness.
-Jan-05-2026-08-00-38-0004-PM.png?width=1200&height=180&name=Ebook%20Banners%20(1)-Jan-05-2026-08-00-38-0004-PM.png)
Is Mexico still competitive despite tariffs and global uncertainty?
Yes. Data shows that manufacturing exports—especially non-automotive—remain resilient and are driving overall export growth, even in a challenging global environment.
Why are non-automotive exports growing faster than automotive exports?
Because sector-specific tariffs are being enforced more strictly on automotive exports, while other manufacturing segments benefit from stronger demand, diversification, and fewer trade frictions.
What should companies evaluate when considering Mexico as an export platform?
Key factors include proximity to the U.S. market, USMCA compliance, infrastructure quality, talent availability, and the ability to integrate into advanced manufacturing and nearshoring-driven supply chains.
-4.png?width=1200&height=179&name=Ebook%20Banners%20(2)-4.png)
-
Economic engine: The manufacturing sector—driven by non-automotive exports, which grew 12.25% in 2025—continues to be Mexico’s primary economic engine, offsetting volatility in other sectors and supporting overall export growth.
-
North American dependence and USMCA risk: The United States remains Mexico’s main export destination (83.9% of non-oil exports). The 2026 USMCA review will be a pivotal moment for safeguarding Mexico’s role in regional value chains.
-
Nearshoring-driven investment: Supply chain relocation could add up to $35 billion USD in exports, making infrastructure investment critical to capturing this opportunity.
-
Automotive sector in transition: The automotive industry—accounting for 24% of exports—must successfully navigate the shift toward electromobility despite tariff-related contractions in 2025. Its adaptation is essential to Mexico’s manufacturing future.
-
Future competitiveness: Maintaining leadership requires moving from cost-based advantages to value-added production through Industry 4.0 adoption and sustained talent development.





